Most cases of small-sized cuts typically heal within a span of a few days unless they end up infected. Even minor scratches on the skin can easily allow bacteria, parasites and viruses to enter the body, causing serious or even life-threatening infections.
The initial indication of infection is usually pain that tends to worsen after the first or second day. After some time, the infected area will turn red in color, swollen and warm or even drain pus. If you suspect that a cut is infected, it is important to provide the appropriate care. You can enroll in a first aid course today so that you know how to provide proper wound care.
Steps in handling a cut with infection
- Carefully assess the infected cut. Check if there are boils or pustules that appear similar to spider bites or bumps that are red in color, swollen, warm and painful since these indicate MRSA (methicillin-resistance staphylococcus aureus) which is a skin infection that quickly spreads to others.
- Check the temperature of the individual using a thermometer. A fever with an oral temperature higher than 101 degrees F among adults usually indicates a serious wound infection.
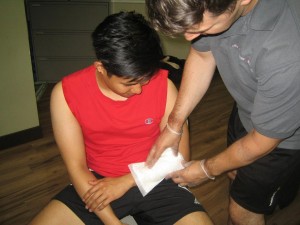
- Wrap an open or draining wound using a sterile bandage and wash your hands thoroughly. Avoid draining, popping open or disinfecting the wound since the infection can readily spread to others. If it is caused by MRSA, it can be hard to manage.
- A healthcare professional should be consulted for instructions. Depending on the age, symptoms, temperature, overall health, depth and location of the wound, the individual might be advised to continue treatment at home or go directly to a clinic or hospital for treatment.
- The instructions given by the doctor should be followed carefully. For a cut that is not deep and not accompanied by fever or signs of MRSA infection, antibiotic cream should be applied or apply a warm, wet compress several times in a day until the wound heals. In case MRSA infection is suspected, the doctor will perform incision and drainage under sterile conditions.
- All the prescribed medications given by the doctor should be taken even if the infection is already getting better. If the medications are stopped without completing the full course, the bacteria are not fully eliminated from the system and can become resistant to the antibiotic, thus making the infection difficult to treat.
In case there is no improvement after 48 hours after of antibiotics, a doctor should be consulted since there might be a change in the antibiotics prescribed or to drain the infection again.
Considerations to bear in mind
Always remember that a skin infection can spread to the joints and bones. Children below the age of three and those who have certain health issues including sickle cell anemia, arthritis, diabetes and hemophilia face a higher risk for developing infections.
The ideal way to prevent a cut from getting infected is to cleanse it using water and soap after the bleeding is controlled. The initial dressing applied should be sterile. If unable to clean the wound thoroughly, a doctor should be consulted.
