A staph infection is generally caused by the Staphylococcus aureus such as pneumonia, skin infections, food poisoning and blood poisoning. It is important to note that the bacteria generally thrives harmlessly on the skin, but once there is a wound, the staph bacteria has an entry and can cause an infection. The skin infections are the most prevalent and can be managed with over-the-counter measures.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ks0QMl9e1hk
Cleansing measures
A localized staph infection in the skin is initially managed with cleansing using antibacterial soap and immersed in warm water. There are also antibacterial soaps available over-the-counter that can help limit the spread of the infection.
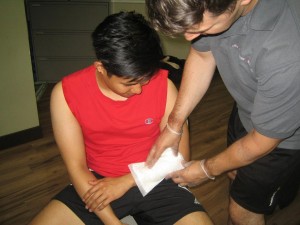
Antibiotics
Antibiotic ointments are ideal topical treatments for a staph infection. Once the affected area has been cleansed and soaked in warm water, dry the site and dab on an antibiotic ointment.
Cover the affected site with clean dressing to prevent the staph infection from spreading. Only use the towels once before washing.
Pain relief measures for a staph infection
Immersing the site of the staph infection or applying a clean, warm compress on the site can relieve the discomfort. Heating pads or warm water bottles can be used at 20-minutes sessions for 2-3 times throughout the day for relief from pain. Over-the-counter pain medications specifically non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are given to lessen the pain linked with a staph infection.
What are the potential complications?
In case a staph infection does not settle, the bacteria can trigger serious issues such as toxic shock syndrome, blood poisoning and even pneumonia.
Other complications might include cellulitis or impetigo. If the infection does not subside in a few days of treatment with over-the-counter remedies or high fever develops or the site becomes warm and swollen, seek medical care right away.
